WINDOW RAILING MANUFACTURER
- HOME
- WINDOW RAILING
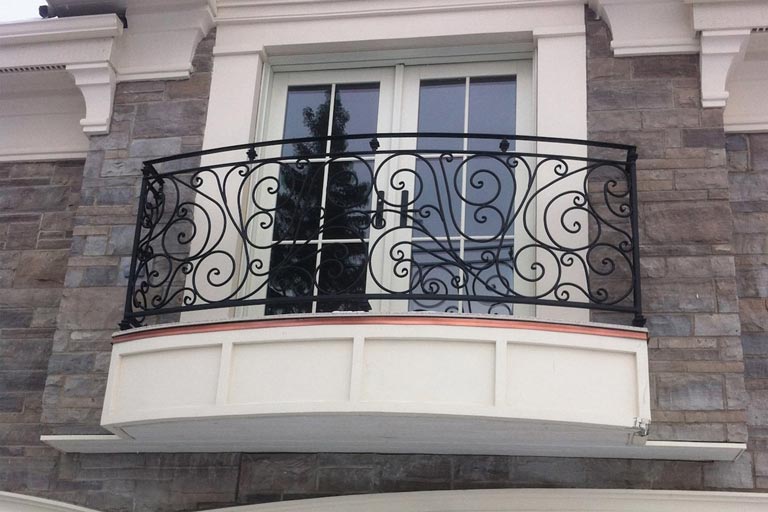

WINDOW RAILING SYSTEM
The term “window railing” is not a standard or widely recognized term in the context of architecture or construction. However, based on the components mentioned, it is possible that the term is used to describe a railing or guardrail system around a window, particularly in elevated or open settings. Here’s a general interpretation:
Possible Interpretation:
A “window railing” could refer to a protective barrier or guardrail system installed around the perimeter of a window, especially when the window is situated in a location where there is a potential fall hazard or where safety concerns are addressed.
OUR WINDOW RAILING SYSTEMS

E42 GLASS BASE SYSTEM

B25 GLASS BASE SYSTEM
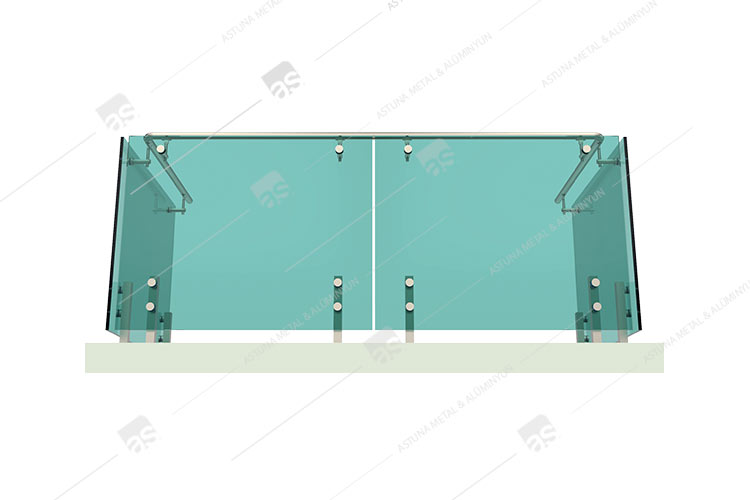
M84 GLASS BASE SYSTEM

AS87 GLASS BASE SYSTEM
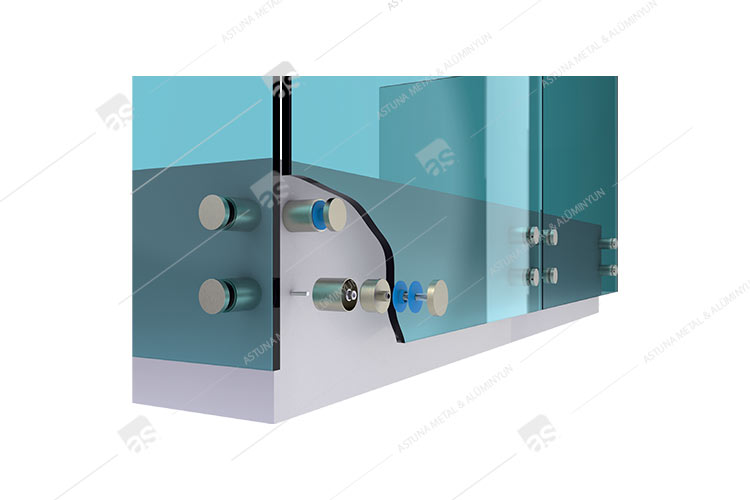
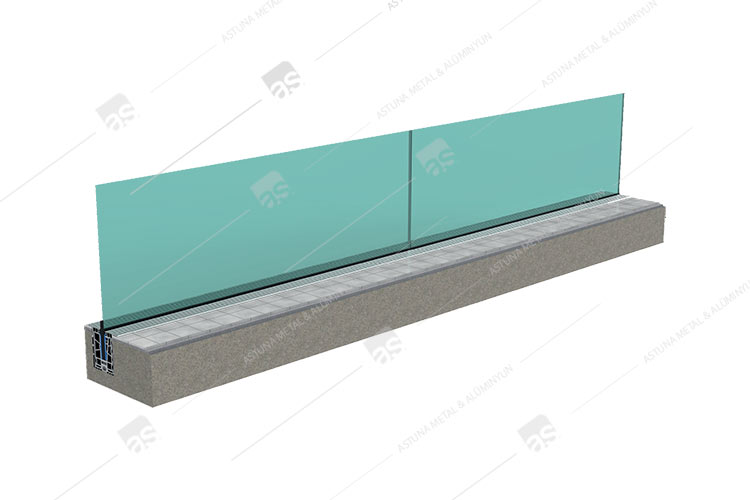
AK61 GLASS ADAPTER SYSTEM

AS20 GLASS BASE SYSTEM

CF33 GLASS CARRIER SYSTEM

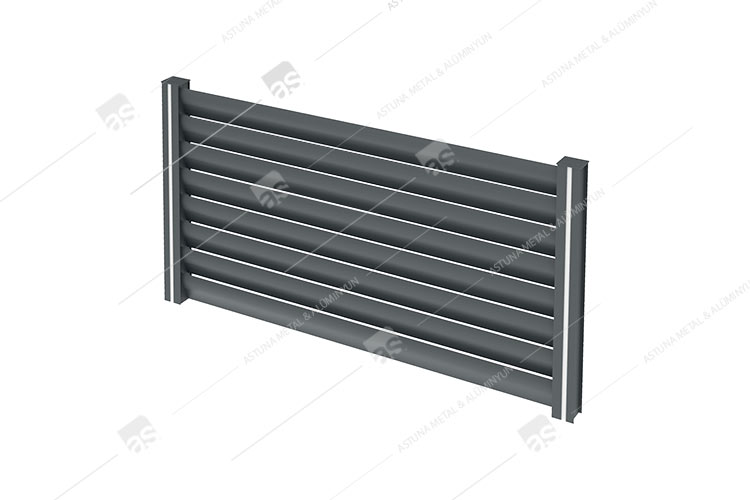
D11 GLASS BASE SYSTEM
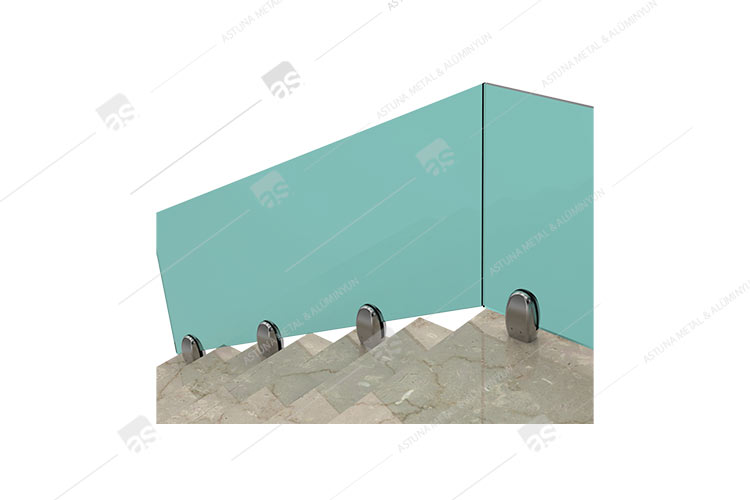
DK10 GLASS CARRIER SYSTEM

K21 GLASS CARRIER SYSTEM

LAMA STRUTS SYSTEM

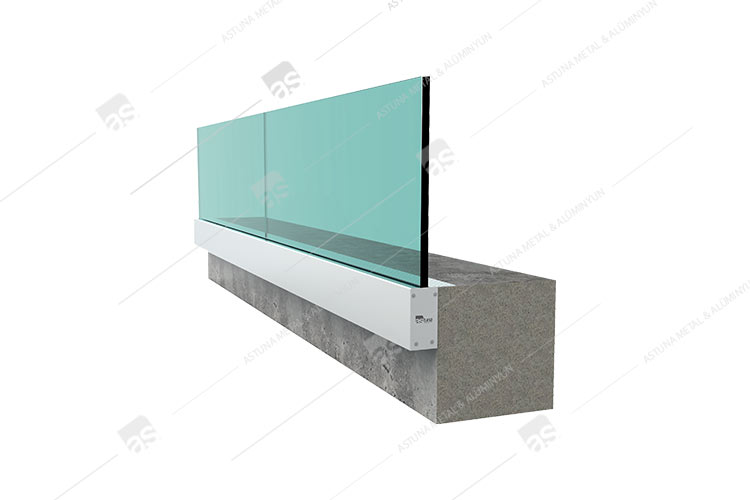
LM20 GLASS CARRIER SYSTEM
KEY FEATURES OF WINDOW RAILING
- Handrail:
- A horizontal rail at the top of the railing system, providing a surface to hold onto for support.
- Balusters (Spindles):
- Vertical posts or rods that connect the handrail and the base rail.
- Base Rail:
- The lower horizontal rail that runs parallel to the handrail, providing additional support and connecting the balusters.
- Newel Posts:
- Vertical posts located at the starting and ending points of a railing section, often serving as anchor points for the railing.
- Balcony or Terrace Window Railing:
- In settings where windows open to balconies or terraces, a railing system might be installed to enhance safety and prevent falls.
- Mezzanine Window Railing:
- For windows located near mezzanine levels or elevated platforms, a railing system may be employed to provide a safety barrier.
- Roof Window Railing:
- Windows on roofs or skylights might have a railing system around them to ensure safety when accessing the roof.
- Decorative Window Guardrail:
- In certain architectural styles, a decorative railing might be installed around windows for aesthetic purposes, although this is less common.
WHAT IS THE USE OF WINDOW RAILINGS?
- Window railings, also commonly known as window guards or window barriers, serve various purposes depending on the specific context of their installation. Here are some common uses and functions of window railings:
- Safety and Fall Prevention:
- One of the primary functions of window railings is to enhance safety, especially in elevated or high-risk areas. They prevent accidental falls from windows, balconies, terraces, or mezzanine levels.
- Child Safety:
- Window railings are often installed in homes, particularly in multi-story buildings, to create a protective barrier that prevents young children from accessing or falling out of windows.
- Building Code Compliance:
- Many building codes and regulations require the installation of window railings in specific situations to ensure compliance with safety standards. This is especially common in residential and commercial buildings.
- Security:
- Window railings can act as a deterrent to unauthorized access or entry, providing an additional layer of security for ground-level or easily accessible windows.
- Aesthetic Enhancement:
- In some cases, window railings are designed for aesthetic purposes to complement the architectural style of a building. Decorative railings can add visual interest to the facade.
- Balcony or Terrace Safety:
- When windows open to balconies or terraces, railings are installed to create a safe enclosure, allowing occupants to enjoy outdoor spaces without the risk of falling.
- Preventing Accidental Window Opening:
- Certain window railings are designed to prevent windows from fully opening, limiting the risk of accidental falls or providing controlled ventilation.
- Code Compliance for Short Windows:
- In regions where building codes stipulate a minimum height requirement for openings, window railings may be installed to bring the window into compliance.
- Roof or Skylight Safety:
- For windows on roofs or skylights, railings provide a safety barrier to prevent falls when accessing or maintaining these areas.
- Safety and Fall Prevention: